Common Factor:
STEMI results in most cases from an occulsive coronary thrombus at the site of a preexisting atheroseclerosis plaque. More rarely, infarction may result from the prolonged vasospasm, inadequate myocardial blood supply. Very rarely myocardial infarction may caused by embolic occulsion, vasculitis, aortic root or coronary artery dissection. Cocaine , a cause of Acute MI with ST-Segment Elevation should be considered in young inviduals without risk factors. A condition that may mimic STEMI is Stress myocardiopathy.
Findings of Clinical Examination:
A
1. Premonitory pain:
Acute MI with ST-Segment Elevation
There is usually is worsening in the pattern of angina precedings the onset of symptoms of mycocardial infacrtion
2. Pain of infarction:
Unlike anginal episodes, most infarction occure at rest , and more commonly in the early morning. The pain is similar to angina in location and radiation but it may be more worse, and it build up rapidly or in waves to maximum intensity over a few minutes or longer. Nitroglycerin has liitle effect, even opioids analgesic may not relieve the pain.


3.Associated Symptoms:
Patient may breakout in cold sweat, feeling of weakness and apprehensive, and move a liitle bit, and try to finds a comfort position. They prefer not to lie quietly. Light headness, syncope, dyspnea, orthopnea, cough, wheezing, nausea and vomiting, or abdominal bloating may be present singly or in any combination.
4.Painless Infarction:
1/3 of patients with acute mycardial infarction present without chest pain, and these patients tend to be undertreated and have poor outcomes. older patients especially women and patients with DM+ are more likely to present without chest pain. As many as 25% of infarctions are detected on routine ECG without any recallable acute episode.
5. Sudden Death and Early Arrhythmias:
50% of the patients death occur before arrive at the Hospital with death presumably caused by ventricular fibrillation.
B. Signs
Acute MI with ST-Segment Elevation
1. General:
Patients may appear anxious and sometime are sweating profusely . The heart rate may range from marked bradycardia (most commonly in inferior infarction ) to tachycardia low cardiac output , or arryhythmia . The BP may high , specially in former hypertensive patients or low in patients with shock. Respiratory distress indicate heart failure. Fever , usually low grade after 12 hours and may present for several days. Acute Myocardial Infarction with ST-Segment Elevation
2. Chest:
The killip classification is the standard way to classify heart failure in patients with acute myocardial infarction and has powerfull prognostic value. Killip Class 1 is the absence of rales and s3, Class 2 is rales that do not clear with coughing over one third or less of lung fields or presence of S3, Class iii is rales that do not clear with coughing over more than one third of the lung fields and Class IV is cardiogenic shock.
3. Heart:
The cardiac examination may vey impressive or avery abnormal. Jugular venous distention reflects RA hypertension, and a KUSSMAUL SIGN (FAILURE OF DECREASE OF JUGULAR VENOUS PRESSURE WITH INSPIRATION) is suggestive of RV infarction. Soft heart sounds may indicate LV dysfunction. Atrial Gallops are the Rule (S4), whereas ventrical gallops ( S3) are less common and indicate significant LV dysfunction. Mitral regurgitation murmurus are not uncommon and may indicate papillary muscle dysfunction or, rarely rupture. Pericardial friction rubs are uncommon in the first 24 hours but may appear later.
4. Extremities:
Edema is usually not present. Cyanosis and cold temprature indicate low outPut. The peripheral pulses should be noted , since later shock or emboli may alter examination.
C. Laboratory Findings:
Cardiac specific markers of myocardial damage include quantitative determination of CK-MB highly sensitive and coventional troponin I , and troponin T. Each of these test amy become positive as early as 4-6 hours after the onset of myocardial infarction and sholud be abnormal by 8-12 hours . Ttroponins are more sensitive and specific than CK-MB.” Highly Sensitive” or ” Fourth Generation” troponin assays, which are not yet widely used in the United states but are the standard assays in most of Europe, have a 10 to be detected earlier, using the o 100 fold lower limit of detection , allowing myocardial infarction to be detected earlier, using the change in value over 3 hours.
Calculating the value of troponins may remain elevated for 5-7 days or longer and therefore are generally not useful for evaluating suspected early reinfarction. Elevated CK-MB generally normalizes within 24 hours, thsu being more helpful for evaluatoin of infarction. Low level elevations of troponin in patients with severe chronic kidney disease may not be related to acute coronary disease but rather a function of the physiologic washout of the marker. While many conditions including chronic heart failure are associated with elevated levels of the high sensitivity troponin assays, these assays may be especially useful when negative to exclude myocardial infarction in patients reporting chest pain.
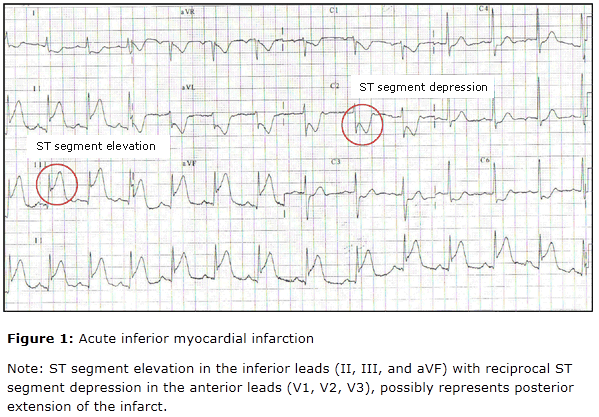
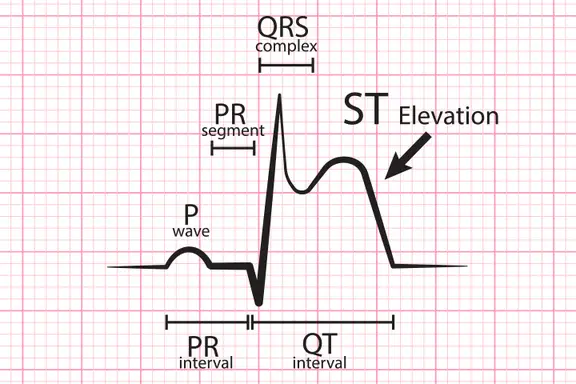
D. ECG:
The extent of the ECG abnormalities, especially the sum of total amount of ST -segment deviation, is a good indicator of the extent of acute myocardial infarction and risk of subsequent adverse events. Th e classic evolution of changes is from peaked (“hyperactive”) T waves, to ST segment elevation , to Q wave development , to T wave inversion. This may occure over a few hours to several days. The evolution of new Q waves 9 longer than 30 mesc in duration and 25% of the R wave amplitude) is diagnostic, but q waves do not occur in 30-50% of acute infarction.
Left Budle branch block especially when new, in patients with symptoms of acute myocardial infarction, is considered to be a “STEMI equivalent”: reperfusion therapy is indicated for the affected patient . Concordant ST elevation ( i.e ST elevation in leads with an overall positive QRS Complex) with left bundle branch block is a specific finding indicating STEMI.
Acute MI Treatment
For treatment please visit “Consult a doctor for free ” page and get treatment of your concerned problem.